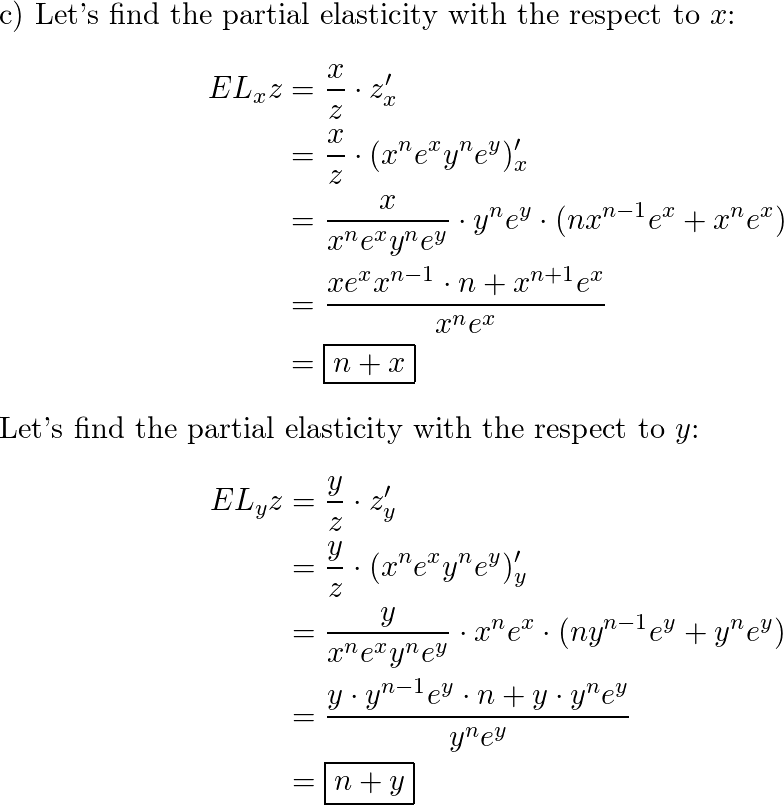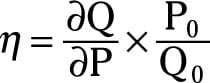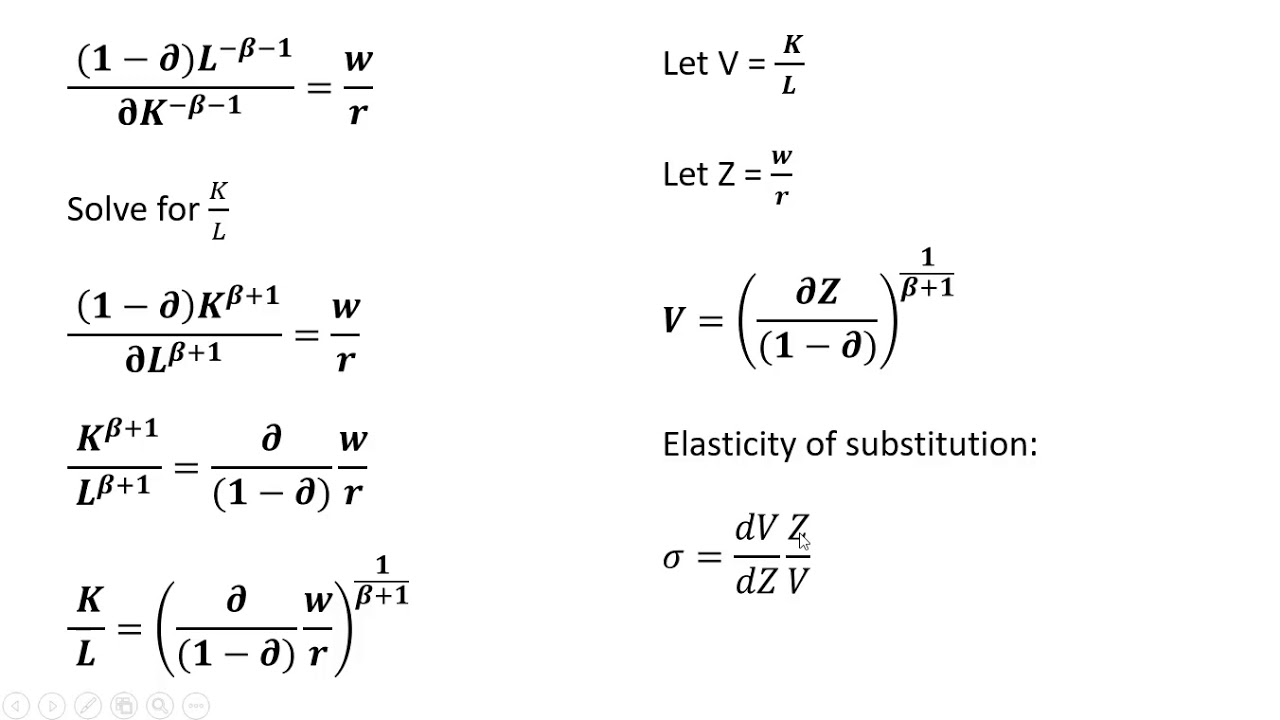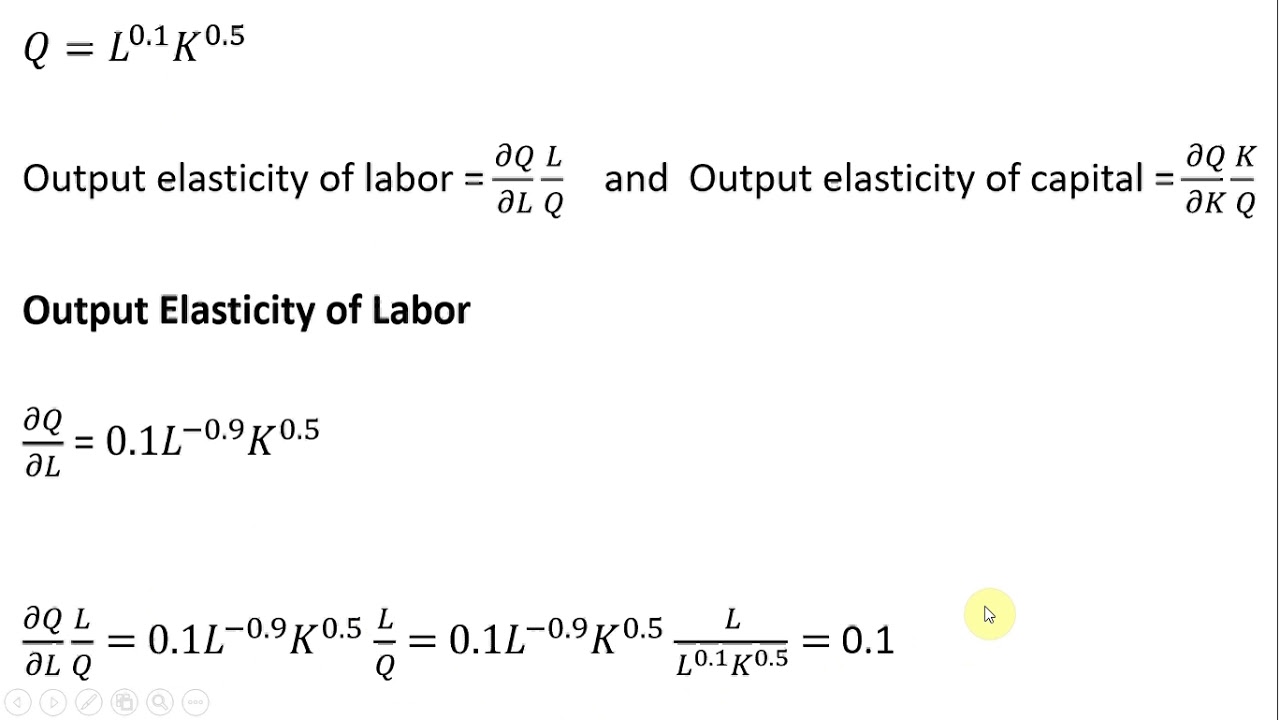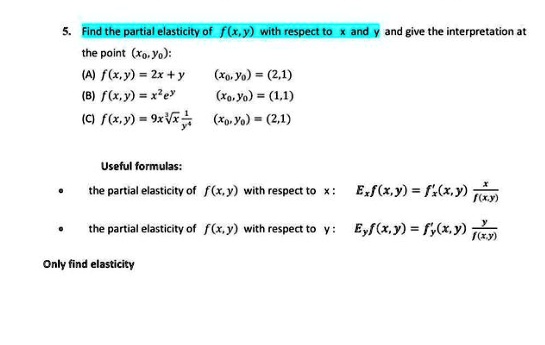
SOLVED: Find the partial elasticity of f(x,y) with respect to x and y and give the interpretation at the point (Xo, Yo): (A) f(xy) = Zx+Y (Xo, Yo) (2,1) (B) f(x,y) =

1 Topic 7 Part I Partial Differentiation Part II Marginal Functions Part II Partial Elasticity Part III Total Differentiation Part IV Returns to scale. - ppt download

Application of Simple & Partial Derivatives | Part-1 | Finding the Price Elasticity of Demand - YouTube

Exercise 6.5: Partial elasticity of demand - Problem Questions with Answer, Solution | Applications of Differentiation | Mathematics

Application of Simple & Partial Derivatives | Part-1 | Finding the Price Elasticity of Demand - YouTube




![5 Elasticity - Solving Partial Differential Equation Applications with PDE2D [Book] 5 Elasticity - Solving Partial Differential Equation Applications with PDE2D [Book]](https://www.oreilly.com/api/v2/epubs/9781119507932/files/images/c05-math-0001.png)